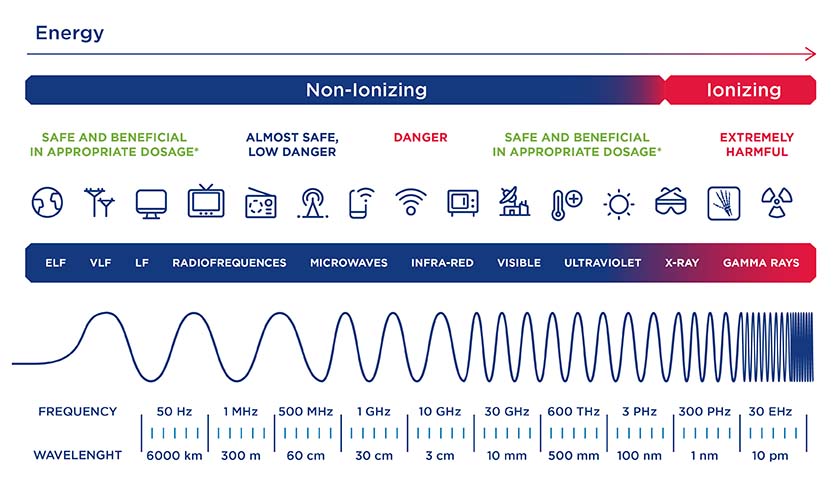
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a form of energy that travels through space at the speed of light. It is produced by many natural and human-made sources, including the sun, the Earth, radio and television broadcasts, and electronic devices.
Electromagn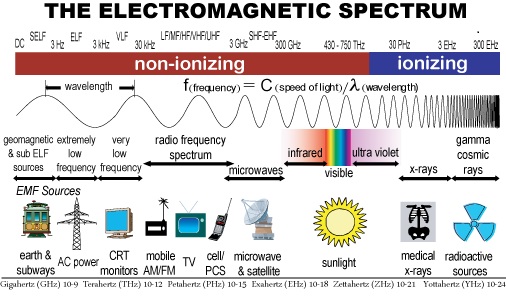 etic radiation can be classified into two types: ionizing and non-ionizing. In this blog, we will explore the differences between these two types of electromagnetic radiation and their potential effects on human health.
etic radiation can be classified into two types: ionizing and non-ionizing. In this blog, we will explore the differences between these two types of electromagnetic radiation and their potential effects on human health.
Ionizing Electromagnetic Radiation
Ionizing radiation is high-energy radiation that can strip electrons from atoms and molecules, ionizing them. This type of radiation has enough energy to break chemical bonds and damage DNA. Examples of ionizing radiation include X-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic rays.
Ionizing radiation is known to cause cancer and other health problems, such as mutations, tissue damage, and cell death. It is also a significant source of radiation exposure in medical imaging, such as X-rays and CT scans. Therefore, it is important to minimize exposure to ionizing radiation and follow safety guidelines when necessary.
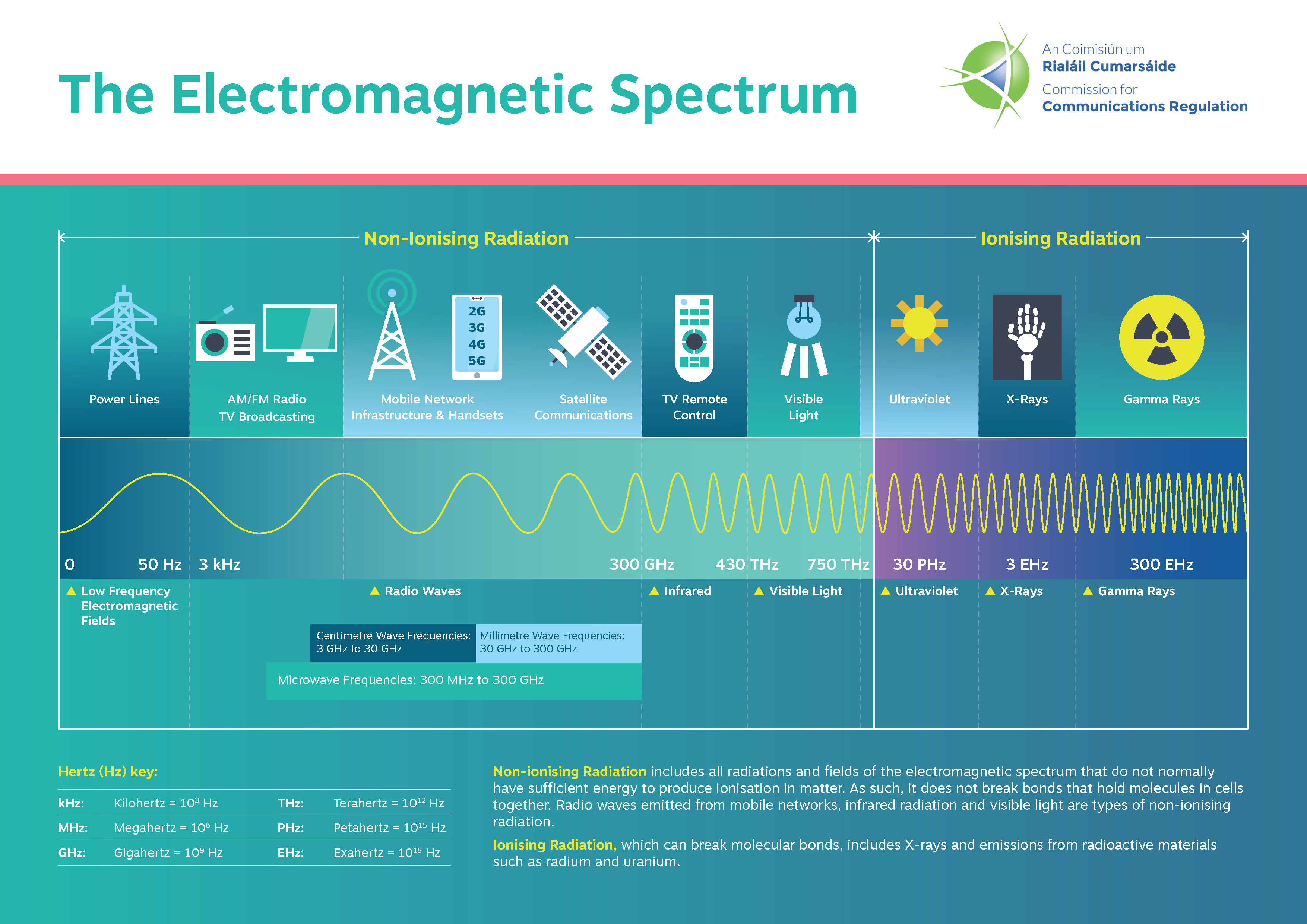
Non-Ionizing Electromagnetic Radiation
Non-ionizing radiation is low-energy radiation that does not have enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules. Examples of non-ionizing radiation include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, and visible light.
Unlike ionizing radiation, non-ionizing radiation is not known to cause cancer or other health problems. However, some studies have suggested that prolonged exposure to non-ionizing radiation may have other effects on human health, such as increased risk of brain tumors, impaired sleep, and reduced fertility.
Cellular phones and other wireless devices are sources of non-ionizing radiation that have raised concerns about potential health effects. There are so much conclusive evidence linking non-ionizing radiation from wireless devices to adverse health effects, therefore health experts suggest taking precautions such as using hands-free devices, limiting cell phone use, and keeping the device away from the body.

Conclusion
In conclusion, electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that can be classified into two types: ionizing and non-ionizing. Ionizing radiation has enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules and cause cancer and other health problems, while non-ionizing radiation does not have enough energy to cause ionization or cancer instantaneously. However, prolonged exposure to non-ionizing radiation may have other effects on human health, and it is recommended to take precautions when using wireless devices. It is important to understand the potential risks and benefits of electromagnetic radiation and to follow safety guidelines when necessary.